Subscribe
The telecommunications industry has undergone tremendous changes in recent years. From the days when consumers could only make and receive voice calls on a landline to the broadband internet era in which people use data and stream videos on the go, telecom networks constitute an important backbone of the national economy.
Telecom networks have evolved from 3G to 4G and 5G technologies. 5G enables connectedness in our world by powering Internet of Things (IoT) devices in new and remarkable spaces, which in turn impacts more of everyday life and business.
How 5G network slicing works
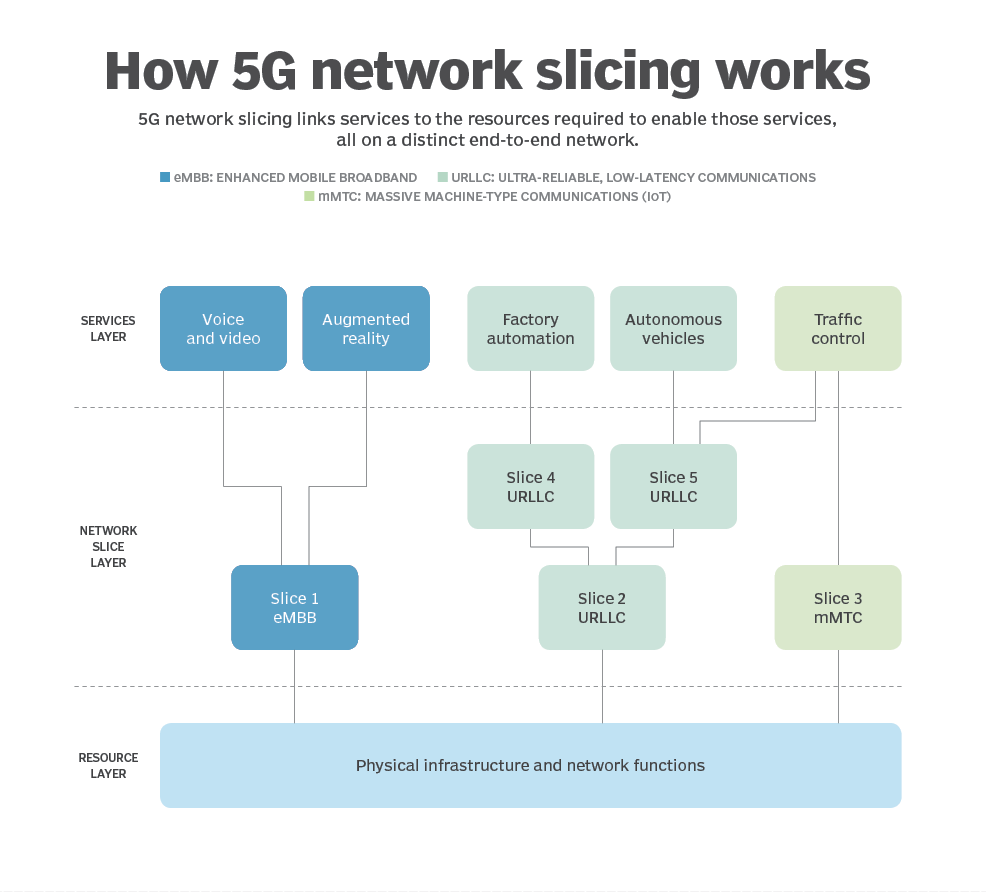
The development of 5G focused on three important concepts related to the fifth generation of mobile technology. These individual slices of network traffic are divided up so the network can link services to the resources required for those services.
- Ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) is used for factory automation and autonomous vehicle services.
- Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) is used for voice, video, and augmented reality services.
- Massive machine-type communications (mMTC) is used for traffic control services.
The basic telecom network architecture is comprised of the base station, the radio access network, and the core network. Radio Access Network (RAN) is currently undergoing three technological transformations.
- Virtualized RAN (V-RAN) is a network architecture that separates the traditional hardware-based functions of a mobile network's radio access system, enabling greater flexibility and scalability through virtualization.
- Cloud RAN (C-RAN) is a network architecture in which baseband processing functions are consolidated in a centralized location, often in a modern cloud like AWS or Azure, allowing efficient resource utilization and improved network management.
- Open RAN (O-RAN) is a network architecture that promotes interoperability and vendor-neutral standards, enabling the use of mix-and-match components from different suppliers to enhance flexibility and innovation in mobile networks.
How to secure the 5G network
With the adoption of O-RAN standards and network architectures, the security needs of telecom networks have never been greater. Defensics®, a comprehensive, versatile, automated black box fuzz testing solution from Synopsys, helps telecommunication networks in four areas.
- Interoperability. Validate that different vendor interpretations of telecommunication protocol and interface specifications can exchange information as intended, and are spec-compliant.
- Robustness. Validate that the implemented telecommunication protocols and interfaces can withstand invalid and out-of-specification inputs (anomalized, fuzzed messages).
- Security. Validate that the implemented telecommunication protocols and interfaces meet a high level of security by focusing on identifying zero-day vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and other potential risks.
- Compliance. Validate that the implemented communication protocols and interfaces meet the fuzz-testing requirements defined in industry standards.
Meeting 5G network compliance standards
Similar to Network Equipment Security Assurance Scheme (NESAS) certification requirements that govern 5G equipment, the O-RAN Alliance has established a set of standards for O-RAN–based products. The O-RAN certification and badging program represents a comprehensive mechanism to ensure confidence in O-RAN based products and solutions for both the operator and vendor communities. It aims to minimize repetition of fundamental and common tests performed to verify and validate O-RAN–based products and solutions before their deployment in operator networks.
The O-RAN badging program mandates fuzz testing before equipment can be bought and deployed by operators. The potential negative impact to critical infrastructure of a network outage due to insecure or noncompliant network components cannot be overstated.
Defensics has been issued three key certificates and badges for its suite of O-RAN test suite offerings, including the O-RAN certificate, O-RAN Interoperability badge, and the O-RAN End-To-End badge. These certificates and badges verify that a product is compliant to O-RAN specifications and are based on O-RAN conformance tests. They prove the interoperability of a pair of products connected via an O-RAN interface and validate that an end-to-end system meets minimum requirements on functionality and security.
Defensics offers the A1-El consumer and producer test suites, designed for testing the robustness of O-RAN A1 enrichment information consumers and producers. The test suites attempt to discover bugs in implementations by sending invalid, incorrect, and malformed JSON. The test suites are intended strictly for automated black box negative testing in an isolated lab environment. Similarly, the A1-P consumer and producer test suites are designed to test the robustness of O-RAN A1 policy consumers and producers.
How Defensics can help
Defensics is the most reliable fuzz testing solution for vendors and operators looking to ensure a smooth transition to the next generation of communications technology. To learn more about how Defensics can help you solve 5G network security challenges.
Continue Reading
Get the best from AI in software development without risking the worst
Sep 15, 2025 | 5 min read
Contextualizing risk in the AI era
Sep 05, 2025 | 5 min read
What you need to know about the NIST Secure Software Development Framework
Aug 12, 2025 | 5 min read
Black Duck Assist: AI code security assistance in your IDE
Aug 05, 2025 | 3 min read









